Diabetes, a name that is not uncommon in modern society, seems to have become a part of our lives. However, when actually asked about its risks, types and ways to deal with it, many people often find themselves at a loss for words. Today, Sejoy will take you into the world of diabetes. Through five fun and practical Q&A sessions, it will lift the veil on the lesser-known facts about diabetes.
Is diabetes either type 1 or type 2?
When it comes to diabetes, many people immediately think of type 1 and type 2. But in fact, the world of diabetes is far more complicated than this. Type 1 diabetes, often referred to as juvenile diabetes, is caused by the destruction of pancreatic beta cells, resulting in an absolute deficiency of insulin secretion. Type 2 diabetes, which is caused by insulin resistance or insufficient insulin secretion, is the most common type of diabetes among adults.
However, apart from these two well-known types, there is a special type known as gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and screening is usually conducted between 24 and 28 weeks of gestation. Due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, some pregnant women may develop insulin resistance, which can lead to hyperglycemia. Although most patients with gestational diabetes will have their blood sugar return to normal after giving birth, the risk of them and their children developing type 2 diabetes in the future will increase.
In addition, there are some special types of diabetes, such as mitochondrial gene mutation diabetes and adult-onset diabetes (MODY), which are relatively rare but equally worthy of attention. Therefore, when we talk about diabetes, it is by no means limited to type 1 and type 2.
2. What are the main symptoms of diabetes and how to identify it?
The symptoms of diabetes are diverse, but not all of them occur simultaneously. Understanding and identifying these symptoms is crucial for the early detection of diabetes.
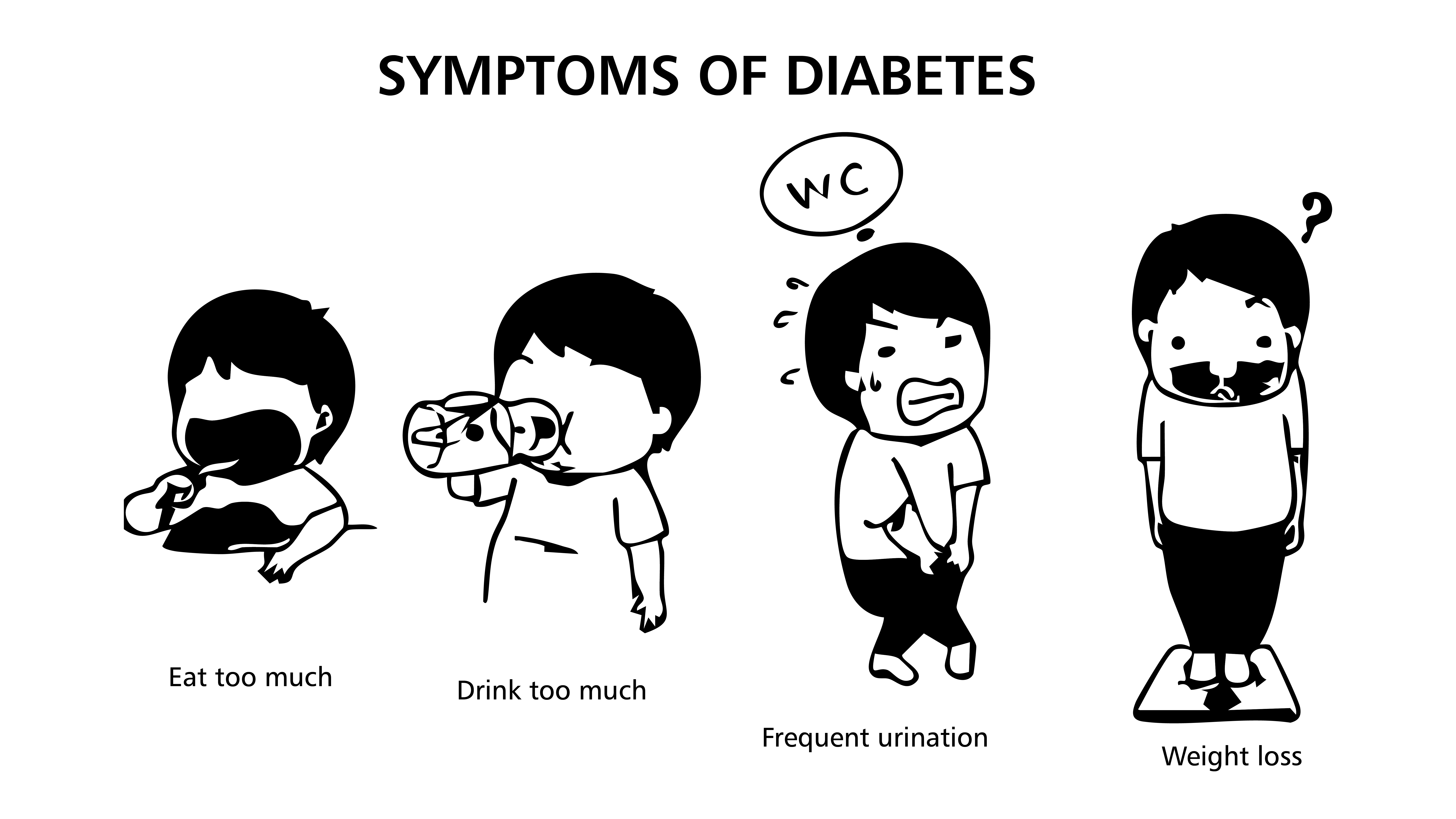
The most common symptoms of diabetes are “three more and one less” : excessive thirst, increased appetite, frequent urination and weight loss. Due to insufficient insulin or insulin resistance, the body is unable to effectively utilize glucose for energy, thereby leading to elevated blood sugar levels. To eliminate excess sugar, the body increases urine output, which in turn causes thirst and excessive drinking. At the same time, as the body cannot obtain sufficient energy from food, the patient will feel hungry, eat more, but lose weight.
In addition to the “three more and one less”, diabetes may also be accompanied by other symptoms, such as blurred vision, slow wound healing, skin infections, fatigue, and breathing difficulties. Although these symptoms may seem ordinary, if they persist or worsen, one should seek medical attention promptly to have their blood sugar checked.
The key to identifying symptoms of diabetes lies in remaining vigilant. If you or your family members experience the above symptoms, especially the “three more and one less”, you should have your blood sugar tested in time to detect diabetes as early as possible.
3. What are the risk factors for diabetes?
The occurrence of diabetes is not accidental but the result of the combined effect of multiple risk factors. Understanding these risk factors can help us better prevent diabetes.
Genetic factors are one of the important causes of diabetes. If there is a history of diabetes in your family, especially among your immediate family members, your risk of developing diabetes will increase. Furthermore, age is also one of the risk factors for diabetes. As people age, the function of pancreatic beta cells gradually declines, insulin resistance increases, and thus the risk of developing diabetes increases.
Apart from genetic and age factors, lifestyle is also an important factor influencing the onset of diabetes. Obesity, lack of exercise, and poor eating habits can all increase the risk of diabetes. Long-term intake of foods high in sugar, fat and salt, along with a lack of dietary fiber and trace elements, can lead to abnormal metabolism in the body and subsequently cause diabetes.
In addition, some diseases and medications may also increase the risk of developing diabetes. Chronic diseases such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia and coronary heart disease, as well as long-term use of certain medications (such as glucocorticoids), may all have an impact on blood sugar.
Therefore, understanding and controlling these risk factors is crucial for the prevention of diabetes.
4. How to prevent diabetes and how to improve lifestyle to reduce the risk of getting the disease?
The key to preventing diabetes lies in improving one’s lifestyle. By adjusting our diet, increasing physical activity and controlling weight, we can effectively reduce the risk of diabetes.
Dietary adjustment is the foundation for preventing diabetes. It is recommended to consume foods rich in dietary fiber, vitamins and minerals, such as whole grains, vegetables, fruits and beans. At the same time, reduce the intake of high-sugar, high-fat and high-salt foods, and avoid overeating. Arrange meals and portion sizes reasonably to keep blood sugar stable.
Increasing physical activity is also an effective way to prevent diabetes. It is recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise every week, such as brisk walking, swimming, cycling, etc. Exercise can enhance the body’s sensitivity to insulin and lower blood sugar levels. At the same time, exercise also helps control weight and reduce the risk of diabetes caused by obesity.
Apart from diet and exercise, controlling weight is also a key to preventing diabetes. Maintaining a healthy weight range and avoiding excessive obesity can help reduce the risk of diabetes. In addition, quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake, maintaining a good state of mind and sleep habits can also help prevent diabetes.
By improving our lifestyle, we can effectively reduce the risk of diabetes. However, please note that these measures cannot be achieved overnight but require long-term persistence. Only by persistently adjusting one’s diet, increasing physical activity and controlling weight can one truly stay away from the trouble of diabetes.
Annual physical examinations are like regular mine clearance. Regularly monitoring blood sugar is equivalent to telling the enemy diabetes: “I’m keeping an eye on you all the time. Don’t even think about sneaking in!” The examination items for blood glucose include fasting blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin. When necessary, blood glucose after glucose load can also be measured.
5. Can diabetes be reversed?
Whether diabetes can be reversed is a topic of great concern. In fact, reversing diabetes is not impossible, but the key lies in early detection and active treatment.
For newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients, especially those with a short course of the disease and still good pancreatic function, it is possible to reverse diabetes through strict dietary control, increased exercise, weight loss and other measures. These measures can improve insulin resistance and restore the function of pancreatic beta cells, thereby bringing blood sugar levels back to normal.
However, it should be noted that the reversal of diabetes is not a one-time solution. Even if blood sugar levels return to normal, patients still need to maintain a healthy lifestyle and monitor their blood sugar regularly to prevent the recurrence of the disease.
For diabetic patients with a long disease course and severe pancreatic islet function impairment, the possibility of reversal is relatively small. However, through active treatment and management, the progression of the disease can still be controlled and the occurrence of complications can be reduced. Drug treatment, insulin therapy, blood glucose monitoring and other measures are all important means of managing diabetes.
Furthermore, with the continuous advancement of medical research, some new treatment methods have also brought hope for the reversal of diabetes. Cutting-edge technologies such as islet cell transplantation and gene therapy are constantly being studied and explored. Although these technologies are still in the clinical trial stage at present, their emergence offers us more possibilities for treating diabetes.
In conclusion, reversing diabetes is no easy task, but it is not impossible. The key lies in early detection, active treatment and long-term management. Through lifestyle improvements, drug treatments and the exploration of cutting-edge technologies, we are expected to bring better treatment outcomes and quality of life to diabetic patients.
Through today’s five Q&A sessions, we believe you have gained a deeper understanding of diabetes. Although diabetes is a common chronic disease, as long as we remain vigilant, actively prevent and treat it, we will surely be able to stay away from its trouble. Let’s join hands and work together to protect our health!
Post time: Jul-23-2025